Regional Director at Cyclone Robotics, Hew Wee Choong, believes that the Asian Century is going to drive RPA, or robotic process automation, growth in this region. “With economic activity centred in Malaysia and Asia itself, human talent becomes critical in fuelling economic growth, and just like anywhere else in the world, it starts to become scarce.”
Hew stated that due to this, many organizations are looking to adopt RPA and automate processes, so as to alleviate the issue of scarce human resource, knowledge retention, and higher staff attrition.
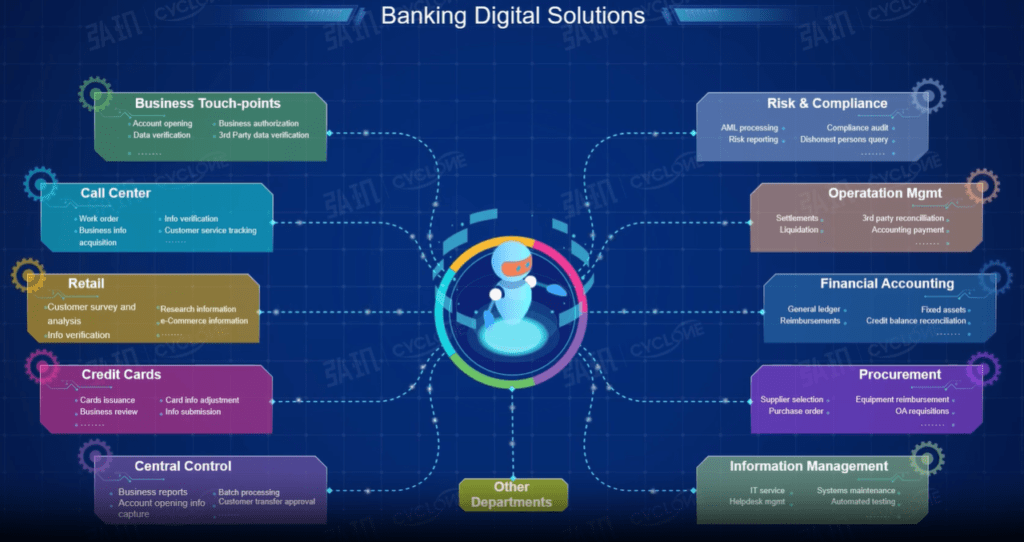
RPA, or Robotic Process Automation, tends to be characterized by automation of basic tasks
It is often used in back office processes like claims processing, customer payment, and these days even backups, onboarding of new staff, and monitoring of networks, according to Hew.
He said, “You will find elements of AI, natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, and even optical character recognition (OCR), and intelligent data processing (IDP) embedded within RPA.” On top of that are other components like computer vision technology that help with for example, automated data entry.
Piloting Artificial Intelligence Generative Automation (AI-GA)

Hew Wee Choong, Head of ASEAN Team, Cyclone Robotics
AI-GA (Artificial Intelligence Generative Automation) which Cyclone Robotics is currently piloting, aims to make it easier for companies to automate processes via natural language, as well as to leverage as much data or knowledge as possible, to do so.
So, AI-GA is built to leverage internal organizational data from siloed systems/documents as well as external sources like certified websites to gain knowledge and automate processes, with or without a human in the process, and with the use of natural language.
“RPA augments customer engagement: It can perform tasks like filtering online comments that need attention and even propose responses based on the content. “
In fact, natural language processing can enhance current RPA usage by enabling more conversational instructions which will be finetuned via continuous machine learning.
RPA in CX and DX
Effort-intensive tasks like transaction processing are ripe for bots to help. RPA bots are already used to contact customers via telephone for further information. Hew even shared about how RPA augments customer engagement: it would filter comments needing attention and even propose replies based on the content.
The company/user could then review the proposed replies and approve them for the bot to automatically post responses in social media. This was presented as a pilot project being developed to both monitor sentiment and engage customers through automated yet relevant responses, and of course, it requires the algorithm being trained for the bot to give appropriate and helpful responses.
In Malaysia, use of bots to respond to inquiries via telephone is also nothing new. Hew added, “You will be surprised to know that even in Malaysia we know of organizations in financial services industry that use bots to make calls and also use artificial intelligence to generate voices.”
In this way also, technologies like AI and machine learning are augmenting and enhancing RPA capabilities.
Perfect Storms
There is a knowledge gap in terms of what RPA can achieve, which throws up a hurdle for organizations to adopt, or fully optimize it.
Use cases like network monitoring, for example. Hew has seen use cases of RPA being used to monitor networks in China, but has not heard of any in Malaysia.
Hew also opined, that in an ideal world single integrated computer systems would be used, instead of separate siloed systems that each contain different domains of information and knowledge. For example customer relationship management (CRM) systems, or finance systems, or human resource, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
The reality is that most organizations have multiple systems like these that are also legacy. RPA is that ‘glue’ that helps connect the information for organizations to achieve digitalization goals, Hew observed.
So, on top of freeing up human resources from mundane tasks and towards high value work that drive innovation, RPA can be that bridge to integrate different legacy infrastructure. And the outcome of this is optimization of current digital capabilities as organizations mature their digitalization levels.
Not forgetting, as more processes are automated more data is also collected which further fuels digitalization using technologies like AI, machine learning, and analytics. That is the goal of hyperautomation which can be defined as automating processes from start to finish and across functional silos in an organization.
Prizing Agility
According to Hew, RPA is a very versatile and agile tool. “So, we see a lot of benefits to adopting RPA. And when we talk to organizations, we focus on these benefits and the objective of implementing automation.”
True, the use of automation capabilities in regulated industries like banking and insurance, must also ensure data is processed accurately and according to compliance requirements without introducing errors.
In this regard, it’s not just about data volume, but how business rules and processing logic are configured to handle the data.
Over time, as more automated processes run and machine learning exceptions are handled, data is accumulated to improve accuracy and expand what can be handled without exceptions.








